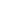Folic acid and folate are two forms of the same, water-soluble vitamin B9. Folate can be found naturally in food, while the folic acid is a synthetic form of this vitamin. It is crucial for synthesis, use and repair of DNA and rapid cell division and numerous other functions of the body. Pregnant women, and those who plan on becoming pregnant are recommended to take folic acid as it prevents miscarriage due to fetal defects such as spina bifida and other complications during pregnancy. It is also quite useful for growing strong and healthy hair, so try adding it to your diet via food, or schedule an appointment with you doctor so he may advise you on taking supplements.
 Folic acid is responsible for metabolism of and balancing the levels of homocysteine in the blood, an amino acid necessary for DNA production and prevention of any alterations to it that may lead to forming of cancer. It is also vital for maintaining adequate brain function, as well as emotional and mental health, prevention of cervical and colon cancer, strokes and heart disease.
Folic acid is responsible for metabolism of and balancing the levels of homocysteine in the blood, an amino acid necessary for DNA production and prevention of any alterations to it that may lead to forming of cancer. It is also vital for maintaining adequate brain function, as well as emotional and mental health, prevention of cervical and colon cancer, strokes and heart disease.
As far as hair health goes, folic acid rejuvenates the cells that promote growth and it works together with vitamin B12 in production of red blood cells, which carry nutrients and oxygen to the scalp and hair follicles, so any deficiency in folates may lead to hair loss.
Deficiency in folic acids affects hair growth in a way, which it leads to impaired cell metabolism, meaning the cells can’t keep up with the production rate of your hair. And as the cells don’t get enough oxygen and nutrients it directly impacts the cells division rate and growth. And lack of nutrients doesn’t only affect the cells in the hair, but the entire scalp, including the papilla and sebaceous glands, or the oil producing cells. This leads to hair that is weak, malnourished and dry hair.
 Foods that contain folates include liver, kidneys, salmon, leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and broccoli, asparagus, beets, tomatoes, beans, peas, a number of roots vegetables, wheat and whole grains, eggs, bananas, avocados and even brewer’s yeast.
Foods that contain folates include liver, kidneys, salmon, leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and broccoli, asparagus, beets, tomatoes, beans, peas, a number of roots vegetables, wheat and whole grains, eggs, bananas, avocados and even brewer’s yeast.
But during food processing, some of that folate is lost, so folic acid is added to replace it, and the foods where this is done are considered enriched foods. Enriched foods include cereals, bread, pasta, flower and rice. Folic acid can be added to foods that already contain nutrients, and those foods are known as fortified foods.
If you may have an underlying medical condition, preventing you from consuming and retaining food or absorbing the nutrients, or just have a deficiency in folates, the best option may be taking supplements. Just make sure to schedule an appointment with your physician or nutritionist before taking them, as the can have a potential for side effects and interactions with other medications.
Folic acid has been known to hide the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency, leading to damage to the nervous system, so it is better to take B complex vitamins than an individual B vitamin.